Summary:
- Heavy rainfall in northern Tanzania led to flooding and landslides, resulting in 47 deaths and 85 injuries, with warnings of a potential increase in the toll, as President Samia Suluhu Hassan orders increased government efforts for rescue operations amid ongoing extreme weather events linked to the El Nino phenomenon in East Africa.
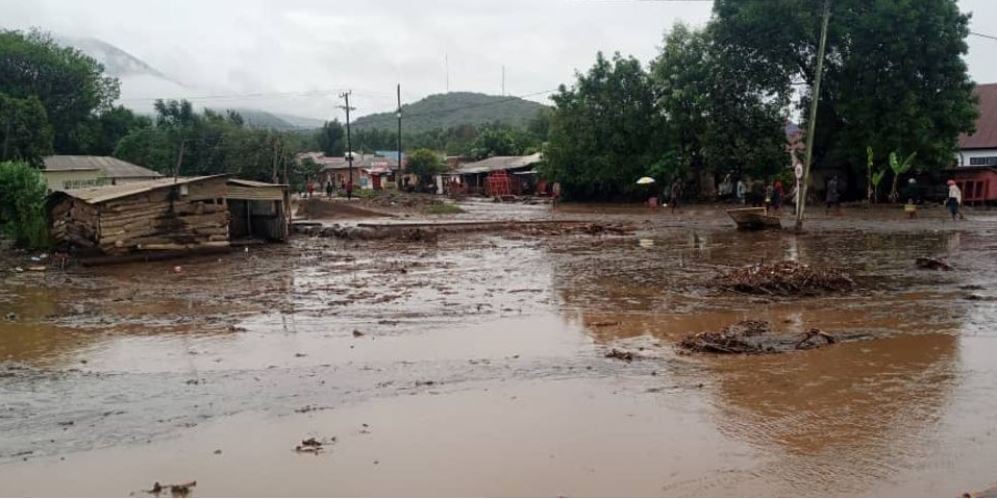
At least 47 people were killed and 85 others injured in landslides caused by flooding in northern Tanzania, a local official announced Sunday, with warnings the toll would rise.
Heavy rain on Saturday hit the town of Katesh, some 300 kilometres (186 miles) north of the capital Dodoma, district commissioner Janeth Mayanja said.
“Up to this evening, the death toll reached 47 and 85 injured,” Queen Sendiga, regional commissioner in the Manyara area of northern Tanzania, told local media.
Let Us Build Your Online Success!
We are the experts in creating visually stunning and functional websites. With reliable hosting and exceptional customer support, we bring your vision to life. Join hundreds of happy clients who trust us!
Get Started Now📞 Call/WhatsApp: +256 207 800 192
Mayanja warned the death toll was “likely to increase”.
Tanzania’s President Samia Suluhu Hassan, in Dubai for the COP28 climate conference, sent her condolences and said she had ordered the deployment of “more government efforts to rescue people”.
After experiencing an unprecedented drought, East Africa has been hit for weeks by torrential rain and flooding linked to the El Nino weather phenomenon.
The downpours have displaced more than a million people in Somalia and left hundreds dead.
El Nino is a naturally occurring weather pattern that originates in the Pacific Ocean and drives increased heat worldwide, bringing drought to some areas and heavy rains elsewhere.
Scientists expect the worst effects of the current El Nino to be felt at the end of 2023 and into next year.
Between October 1997 and January 1998, massive flooding exacerbated by heavy El Nino rains caused more than 6,000 deaths in five countries in the region.
Scientists say extreme weather events such as flooding, storms, droughts and wildfires are being made longer, more intense and more frequent by human-induced climate change.